Blood Clot in the Leg: Deep Vein Thrombosis Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
 By: by Amino Science
By: by Amino Science
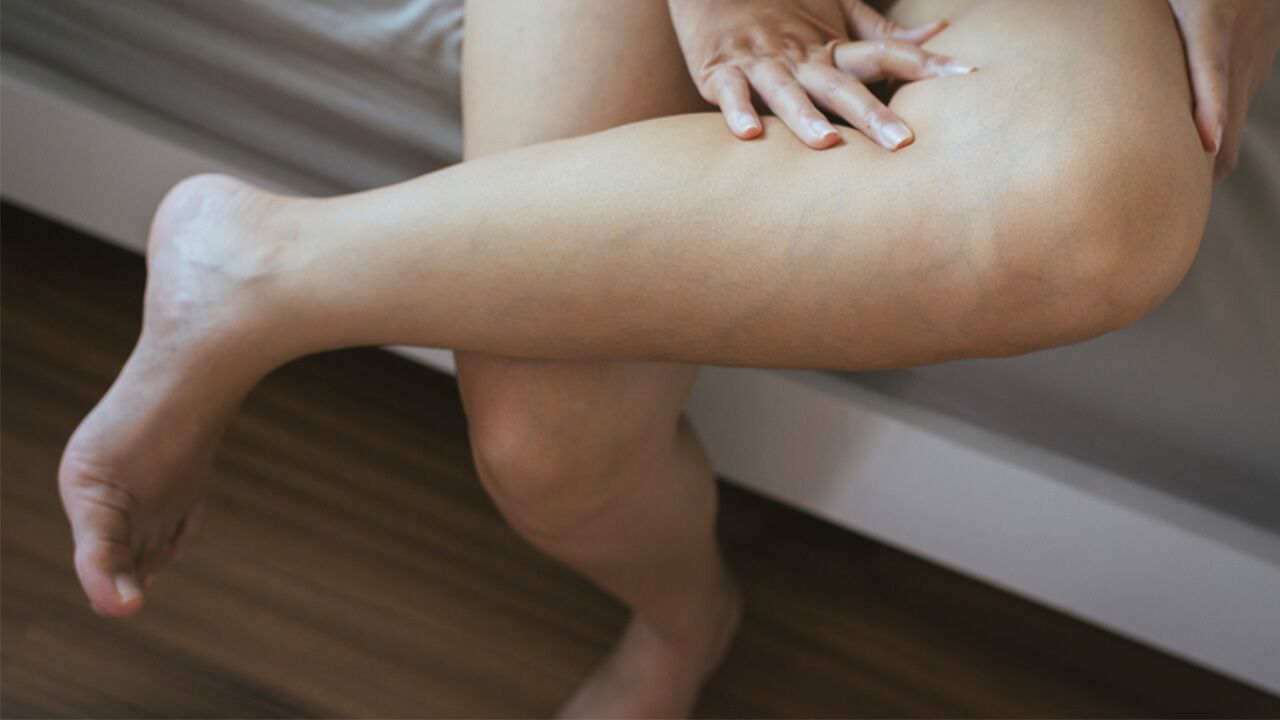

Blood clots are clumps of blood that have changed from a liquid to a gel-like or semisolid state. They are beneficial in stopping bleeding and preventing people from losing too much blood when they are injured or cut. Blood clotting in the leg is the most common scenario.
When a clot forms inside one of the veins, it may not dissolve on its own, creating a potentially dangerous and even life-threatening situation. While an immobile blood clot is usually harmless, it can break free, travel through the veins to the heart and lungs, get stuck, and prevent blood flow, creating a medical emergency. A health care professional needs to look at the symptoms and medical history and determine an appropriate course of action.
Differences in Artery Clots and Vein Clots
The circulatory system contains veins and arteries that carry blood throughout the body. Blood clots can develop in both these types of vessels.
A blood clot that forms in an artery is called an arterial clot. It causes immediate symptoms, such as severe pain, paralysis of parts of the body (or both), and requires emergency treatment to prevent a heart attack or stroke.
A blood clot that forms in a vein is called a venous clot. While these clots usually build up more slowly over time, they can be life-threatening.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), the most serious type of venous clot, forms in one of the major veins deep inside the body. It can happen in a leg, typically the lower leg, an arm, the pelvis, lungs, or brain. It can then travel through the bloodstream and become lodged in the lungs, a condition called pulmonary embolism (PE). Collectively DVT and PE are known as venous thromboembolism (VTE), a potentially fatal medical condition.
Injuries and problems inside blood vessels can lead the body to form blood clots. They develop when a mass forms as a result of plasma proteins and platelets coagulate.
At such time as these clots develop, it is possible that they will migrate elsewhere in the body, triggering harmful reactions. Such is the case with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) when it travels to the lungs and sparks pulmonary embolism (PE). According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), DVT and PE impact as many as 900,000 Americans annually. About 100,000 Americans die from these conditions every year.
Knowing the most common symptoms and risk factors and seeking medical advice in a timely manner can help save your life or the life of a loved one. Unfortunately, blood clots may not manifest any symptoms, or the symptoms can mimic those of other diseases. Nonetheless, it is important to get medical attention if symptoms do appear. The chance of having a blood clot increases if the symptoms are isolated on one leg or one arm.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Causes
Certain risk factors increase the probability of having a blood clot. If a person has a recent hospital stay, especially a long one or one related to a major surgery, the risk of blood clots is much higher. Moderate risk factors include age, especially for people over 65; long trips, especially when sitting for more than 4 hours at a time; bed rest or being inactive for long periods of time; obesity; pregnancy; smoking; birth control pills; and a family history of blood clots.
Some forms of cancer increase the risk of a blood clot fourfold. Chemotherapy increases the risk as much as six times.
Symptoms of DVT
Diagnosing a blood clot by symptoms alone is very difficult. According to the CDC, nearly 50% of people with a blood clot in the leg (or deep vein thrombosis) have no symptoms. While an asymptomatic blood clot is usually a sign that the thrombosis has not yet reached a serious stage, this may not be the case. Even large blood clots needing immediate medical attention can sometimes cause no symptoms at all until the clot dislodges and travels through the bloodstream.
Let’s take a more detailed look at some symptoms of blood clots.
Skin Discoloration
Because of dense collections of blood under the skin surface, discoloration is one of the first warning signs of clot formation in a vein. When deep vein thrombosis skin redness persists over time or intensifies, it is time to seek medical attention.
Painful Swelling
When a blood clot forms, the clot site may swell up. This is particularly likely if the clot is in the calf, ankle, or leg. Because these areas have greater bone and tissue densities, it is harder for the body to clear a clot that is already forming. Swelling from a clot does not respond to treatments such as hot or cold compresses. It also becomes intense and happens without external injury to the affected area.
Skin Warmth
In blood clots in the leg, the skin near the area becomes warm to the touch. Sometimes, there is a persistent feeling of heat or tingling in the localized area.
Pain at the Blood Clot Area
Blood clots may bring on itchiness and throbbing that increase over time if not treated.
Dizziness
Fainting and dizzy spells are evidence that the body cannot dissolve the blood clot naturally or that the blood clot is migrating toward the lungs. There may be labored breathing as well.
Fatigue
When the leg clot gets bigger, the body will try to remove it. Vital organs, such as the heart, will work and pump harder, resulting in an accelerated heartbeat. If the blood clot leaves the leg, there could also be acute, stabbing chest pains that worsen with deep breathing. Increased heart rate can also trigger anxiety and panic attacks. Because the body’s defense systems are working extremely hard, there may be fatigue or exhaustion. Fatigue can be nonspecific and have no apparent cause.
Fever
A mild or low-grade fever can be the result of a blood clot breaking free and entering the bloodstream. There may also be sweating or shivering, an intense headache, body weakness, dehydration, and decreased appetite. As a result of a very high fever between 103 and 106 degrees, one might experience irritability, mood swings, confusion, convulsions, and hallucinations.
Distended Veins
Sometimes the skin surrounding the clot is tender to the touch with no evidence of bruising. Veins may become visible, but that usually happens when the blood clot becomes fairly large. Some blood clots manifest as distended veins near the area where they are developing. Most distended veins will not present complications, but a blood clot that is putting great pressure on surrounding blood vessels can cause internal ruptures.
Foot or Leg Pain
Deep vein thrombosis can cause foot pain. Because the blood clot in the leg is restricting blood flow, the tissues in the feet are being deprived of oxygen. Deep vein thrombosis leg pain can manifest as calf pain that might be mistaken for a muscle cramp. Deep vein thrombosis leg pain is most acute when a person is walking, bending, or flexing the foot upward.
Pale Foot or Ankle
Blood clots can also make the foot or the ankle pale because of decreased blood flow. These areas may turn blue and feel cold.
Coughing
A persistent, but unexplained cough can signal a pulmonary embolism when the blood clot has detached and migrated to the lungs. The cough may be dry, and it is sometimes accompanied by mucus or blood discharge.
Chest Pain
A pulmonary embolism can cause chest pain that feels like a heart attack. It may also cause shortness of breath.
Tests for DVT
Tests rule out other problems or confirm the diagnosis of DVT.
- Duplex ultrasound: For this noninvasive and painless DVT test, the doctor spreads warm gel on the skin and rubs a sensor over the area where the clot might be. The sensor sends sound waves into the body, relays the echoes to a computer, and obtains pictures of blood vessels and blood clots.
- Venography: This is a special X-ray in which the doctor injects a radioactive dye into a vein on the top of the foot to enable the visualization of veins and clots. It could cause more blood clots.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI uses radio waves and a strong magnetic field to create detailed pictures of the inside of the body on a computer. MRI can find DVT in the pelvis and thigh, as well as provide imaging for both legs at the same time.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment
DVT is treated with blood thinners and compression stockings. Graduated compression stockings help to increase blood flow in the legs and reduce swelling. Blood thinners prevent clotting, but can cause serious bleeding. They can be stopped without any change in dose, and their effect lasts for several days. People are likely to need preventive blood thinners and compression stockings during a hospital stay.
Moderate exercise such as walking or swimming is recommended for post-DVT therapy. A return to one’s normal exercise routine depends on the physical condition before the clot and the severity and location of the clots. Exercise boosts circulation, lowers symptoms of venous insufficiency, and usually invigorates people. Aerobic exercise can bolster lung function after a pulmonary embolism.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Prevention
To help prevent deep vein thrombosis, avoid sitting for long periods of 2 hours or more. Take breaks and get up and walk to keep blood moving. During long-distance airplane travel, sit in seats that allow you to get up periodically and walk the aisle. For long car trips, stop and walk around frequently. Crossing one’s legs also interferes with circulation.
It is important to drink fluids when traveling, and all the time. Dehydration can lead to DVT.
Lifestyle changes can prevent blood clots. People can help themselves by losing weight, reducing high blood pressure, stopping smoking, and exercising regularly. Experts also recommend essential amino acids as a nutritional intervention to support healthy blood flow and help preserve heart strength and function.

Up to 25% off Amino
Shop NowTAGS: conditions
Join the Community
Comments (0)
Most Craveable Recipes


 833-264-6620
833-264-6620



















