Metformin for Anti-Aging: The Next Big Break in Healthcare
 By: by Amino Science
By: by Amino Science
The drug metformin has been shown to alter inflammation pathways in the body, which means it can target aging symptoms and remove the exacerbation caused by oxidative stress in conditions like dementia, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. With human testing just getting underway in a study called Targeting Aging with Metformin (TAME), metformin for anti-aging and the treatment of chronic diseases may be the next big breakthrough in healthcare.
What Is Metformin? How Does It Work?
Metformin is currently used as a diabetes drug to help control blood sugar levels for those with type 2 diabetes (but not type 1). It's been managing diabetes since the 1950s in the United Kingdom (and since the 1990s in the U.S.) and is even safe enough for pregnant women to take in cases of gestational diabetes. Metformin is the most commonly prescribed diabetes medication.
Metformin, also known as Glucophage tablets, is metformin hydrochloride, derived from a substance found in French lilac, a type of flowering plant. It's classified as a biguanide medication, able to lower the amount of sugar in the blood in instances of insulin resistance.
When a person with type 2 diabetes can't control their blood sugar levels via diet and exercise, metformin may be prescribed. However, the effect of metformin on human health goes far beyond blood sugar control.
Recent studies have found that metformin also boosts AMPK activity (AMP-activated protein kinase) and reduces the free radical superoxide via the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) protein expression. This reduces inflammation throughout the body and helps prevents DNA mutation and damage, two huge contributors to the aging process. The use of metformin, therefore, may increase life expectancy in aging adults.
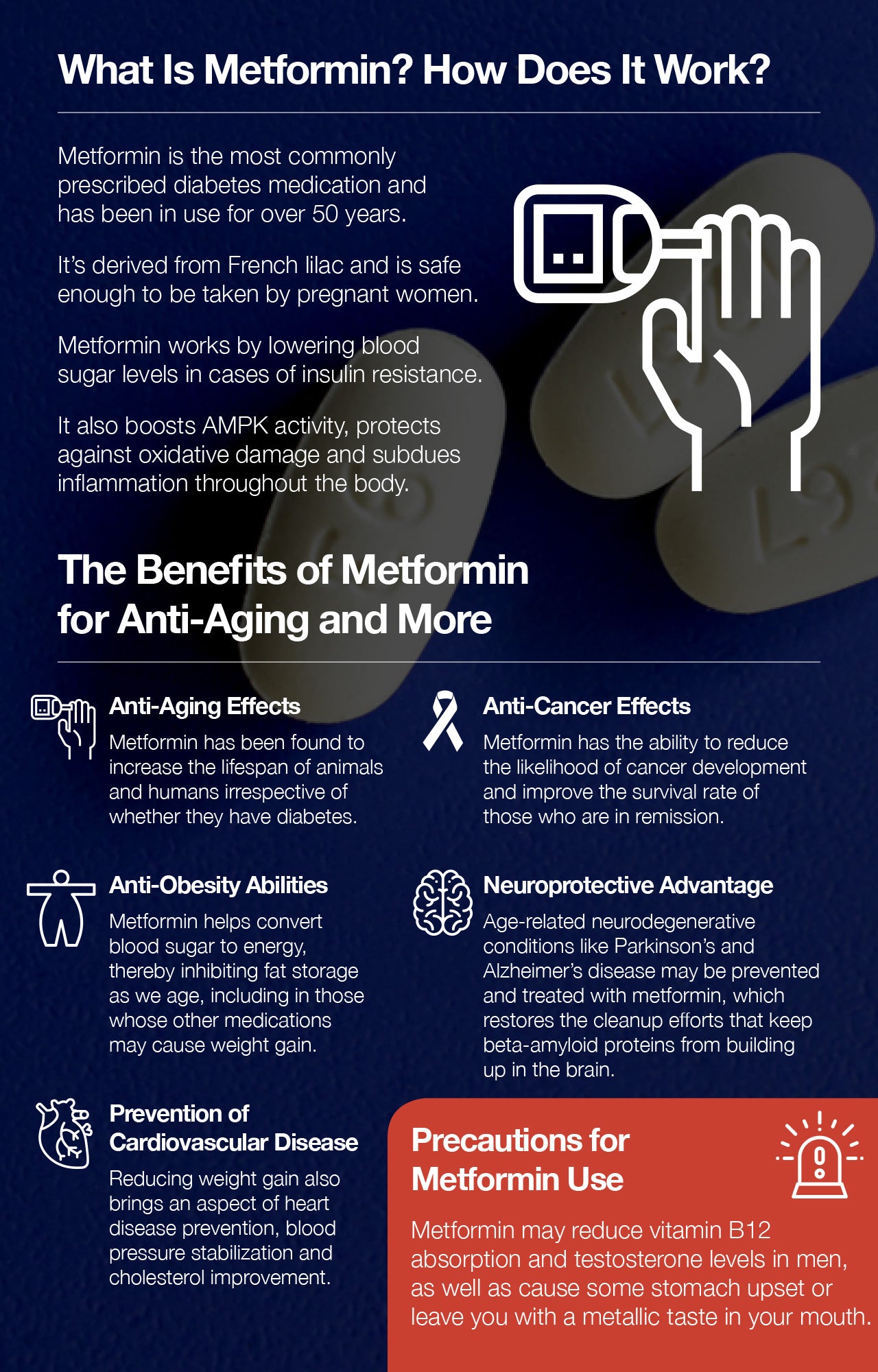
The Benefits of Metformin for Anti-Aging and More
In gerontology, which is the study of old age and the impact of aging on humans, the quest for longer lives is always at the forefront. While the low-cost generic version of metformin has been used for years to activate AMPK and lower blood sugar levels, scientists have recently found that the health benefits of this drug extend to reversing certain effects of aging and are now attempting to get it recognized as the first truly anti-aging drug. A new clinical trial has been approved by the FDA to explore the anti-aging applications of metformin and is the first step in what could be the discovery of the century. Here are the proven abilities of metformin so far.
1. Anti-Aging Effects
According to researchers, metformin can inhibit or reduce many factors that accelerate aging, including chronic inflammation, DNA damage, and weakened mitochondrial function. By promoting the signaling cells AMPK and mTOR, metformin helps reduce sugar and fat storage and encourages our cells to return to their youthful levels of functioning. This positively impacts the human lifespan and helps prevent some of the most dangerous age-related diseases. These discoveries began with animal studies and progressed to human trials.
- Roundworms given metformin lived 20% longer than the control group thanks to the increase in AMPK activity.
- Mice that were administered metformin lived 6% longer than mice in the control group.
- Human participants taking metformin as an antidiabetic drug ultimately lived 15% longer than matched non-diabetic adults.
Because our AMPK activity, like so many other vital processes, declines with age, a drug like metformin that can safely restore AMPK functioning helps reverse the aging of our cells. This effect is irrespective of whether or not you have diabetes, as AMPK is involved in all of our tissues, and metformin offers broad-spectrum support against conditions like obesity, cancer, heart disease, and even neurodegenerative conditions.
2. Anti-Obesity Abilities
If you've ever wondered why getting older often means getting fatter, it's because the youthful behavior of our cells is to burn fat, while age causes our cells to store fat. By activating AMPK, metformin helps to remove sugar from the blood for use as energy, which has the positive side effect of reducing body fat storage and preventing or reversing obesity.
This effect occurs in non-diabetic populations and in people with conditions that almost invariably lead to weight gain, such as women with polycystic ovary syndrome. One study showed that patients with polycystic ovary syndrome who were given metformin for 6 months enjoyed significant reductions in blood sugar levels and weight, losing an average of about 9 pounds, and also had higher levels of "good" HDL cholesterol. The control group, on the other hand, saw increases in their blood sugar and weight levels.
That's not the only unique challenge that metformin has overcome. It has also been effective in lowering the insulin resistance and the body mass index (BMI) of those taking antipsychotic drugs like quetiapine, risperidone, aripiprazole, and olanzapine. Some of the major side effects of these drugs include insulin resistance and rapid weight gain, but metformin can help counteract those effects.
Metformin has also shown similar effects in perfectly healthy adults looking to combat weight gain in middle age and beyond. Researchers found that when healthy participants took metformin they lost more than 11 pounds in 1 year, a significant amount of weight loss that could possibly prevent the development of obesity and all the complications of metabolic syndrome that come with it.
Metformin can even help improve the weight profile of young people, specifically teenagers who may be able to avoid a lifetime of medical issues if they can reign in their weight at that developmental age.
3. Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease
Often hand-in-hand with obesity comes the threat of cardiovascular disease. With all of the cholesterol-lowering drugs on the market, adults in the United States are still dying as a result of heart disease in shocking numbers. Atherosclerosis, a hardening of the arteries due to fat and plaque buildup in the bloodstream, is the most common culprit. Metformin can help prevent such buildup before it happens.
Again, this ability is attributed to metformin's AMPK activation, which mitigates LDL cholesterol oxidation, reduces fat accumulation in blood vessels, and facilitates cholesterol exportation out of cells. On top of all that, metformin helps protect our endothelial cells, the cells that make up the lining of our blood vessels, helping them resist fat penetration and prevent the endothelial dysfunction that is one of the main precursors to atherosclerosis.
There are multiple human studies showing metformin's effect on heart health. A 2016 study found that it helped reduce the systolic blood pressure of non-diabetic participants. In another study it helped reduce the risk of dying by 75% in heart attack survivors during the first month of recovery. Metformin reduces the risk of atrial fibrillation, stroke, and death from all adverse cardiovascular events.
4. Anti-Cancer Effects
Not only do diabetics have an increased risk of developing neck and head cancers, a risk that metformin can reduce up to 46%, but metformin can also reduce gastric cancers by 55%. Non-diabetic patients can also experience this boost, as was found in this massive analysis of studies comprising more than 24,000 participants taking metformin. Results showed a 37% improvement in the rate of recurrence and a 31% improvement in overall survival in cases of colon and rectal cancers. Roughly the same was found in incidences of prostate cancer, with a 17% improvement in recurrence-free survival and an overall survival rate improvement of 18%.
Metformin's anti-cancer ability has been studied in cases involving 17 distinct organs, with an 86% improvement of cancer inhibition across the board, with no evidence showing a risk that it may stimulate any form of cancer. It's a safe and effective prevention method.
5. Neuroprotective Advantage
The effects of metformin on the biomarkers of human aging can potentially prevent age-related neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. By restoring AMPK activity to more youthful levels, the buildup of proteins in the brain cells which characterizes neurodegenerative diseases can be cleaned up more effectively. Specifically, metformin helps to lower levels of enzymes that produce beta-amyloid proteins, decrease the impact of beta-amyloid on brain cell functioning, reduce the levels of the protein alpha-synuclein, and prevent the loss of dopamine-producing cells in Parkinson's cases.
One study found that taking 2,000 milligrams of metformin each day for a year helped older adults with amnestic mild cognitive impairment (a precursor to Alzheimer's) improve their memory recall. There's a form of diabetes specifically associated with Alzheimer's disease known as type 3 diabetes, making this aspect of a leading diabetes medication all the more important.
If you've noticed a similarity in metformin health benefits and the wellness gains of essential amino acids you're on to something! Essential amino acids have also been shown to have anti-aging, anti-obesity, anti-cancer, anti-heart disease, and neuroprotective effects. And you can get your hands on the most trusted essential amino acid supplements here!
Precautions for Metformin Use
Although metformin is incredibly safe considering all that it can do to improve cancer, diabetes, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders, it's still important to know that metformin can disrupt vitamin B12 absorption and may increase levels of homocysteine (another risk factor for cardiovascular disease). A physician may recommend a B-complex supplement or prescription, as normal amounts of the vitamin B12 in foods most likely will not provide enough to counteract this issue.
Moreover, some studies have noted that metformin may reduce testosterone levels in men, which is necessary in cases of diabetes to help increase insulin sensitivity and glucose utilization. This, too, may need supplemental assistance.
Other potential side effects include a buildup of lactic acid levels in the blood (lactic acidosis), gastrointestinal discomfort, and a metallic taste disturbance.
Meeting Metformin
The Food and Drug Administration's allowance of metformin for testing is the first anti-aging study ever approved. It is set to study 3,000 participants over 6 years to either validate or refute results from previous investigations including those conducted by Dr. Nir Barzilai at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine and the American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR). We will have to wait to see the verdict on whether metformin can help extend the lifespan of those who take it. Does the drug prevent the development of age-related cognitive and cardiovascular diseases? Does it stop cancer before it even starts? We're on the frontline of finding out if there truly is a cure to growing older. Stay tuned!

Up to 25% off Amino
Shop NowTAGS: supplements
Join the Community
Comments (0)
Most Craveable Recipes




 833-264-6620
833-264-6620



















